by Ria Olivier | Apr 25, 2025 | Antarctica, Gough Island, International Days, Marine Protected Area, Marion Island, Mice Eradication, Ornithology, Research, SANAP
 Every year on April 25th, we celebrate International Penguin Day—a global reminder of the unique role penguins plays in our planet’s ecosystems. These birds are not just symbols of the icy South—they are indicators of ocean health and climate change. From the sub-Antarctic islands to the Antarctic continent itself, penguins serve as sentinels of the sea, helping scientists track environmental shifts that affect us all.
Every year on April 25th, we celebrate International Penguin Day—a global reminder of the unique role penguins plays in our planet’s ecosystems. These birds are not just symbols of the icy South—they are indicators of ocean health and climate change. From the sub-Antarctic islands to the Antarctic continent itself, penguins serve as sentinels of the sea, helping scientists track environmental shifts that affect us all.
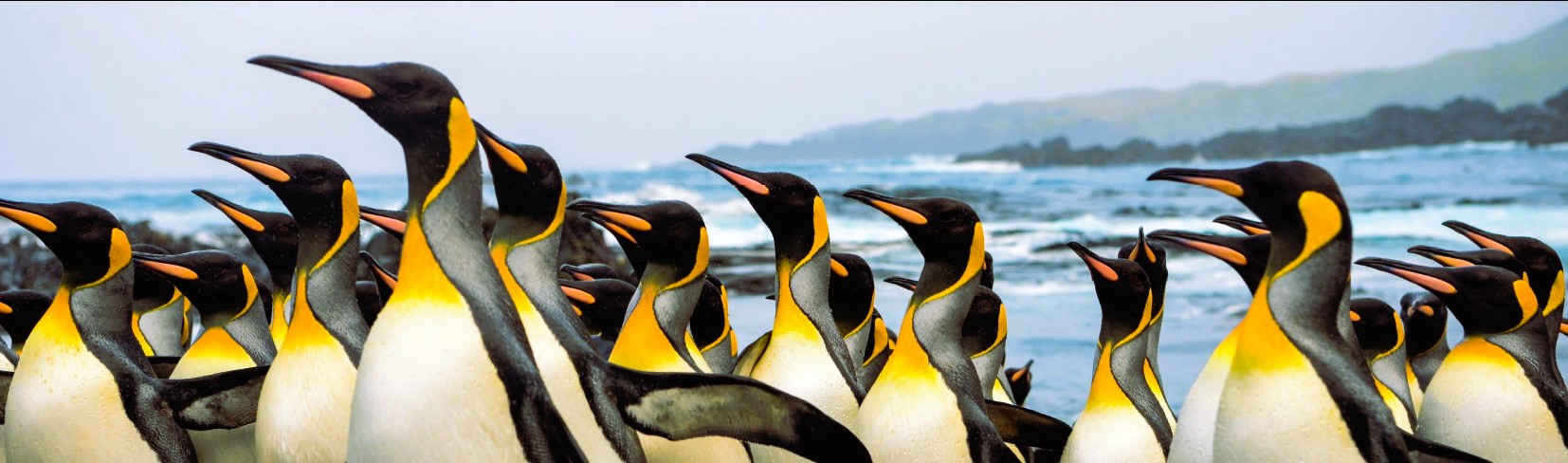 South Africa plays a vital role in this mission through its National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), which supports long-term ecological research at key sites such as Gough Island, Marion Island, and Antarctica. These research stations are crucial hubs for studying penguin populations like the Northern Rockhopper on Gough Island and the Macaroni penguins on Marion Island. Scientists monitor breeding patterns, foraging behaviour, and survival rates—data that provide early warnings about oceanic changes. In Antarctica, SANAP researchers study Adélie and Emperor penguins, whose survival is intimately tied to the health of sea ice and krill populations.
South Africa plays a vital role in this mission through its National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), which supports long-term ecological research at key sites such as Gough Island, Marion Island, and Antarctica. These research stations are crucial hubs for studying penguin populations like the Northern Rockhopper on Gough Island and the Macaroni penguins on Marion Island. Scientists monitor breeding patterns, foraging behaviour, and survival rates—data that provide early warnings about oceanic changes. In Antarctica, SANAP researchers study Adélie and Emperor penguins, whose survival is intimately tied to the health of sea ice and krill populations.
 By investing in these research efforts, South Africa not only contributes to global conservation science but also highlights the importance of protecting our shared polar heritage. This International Penguin Day let’s celebrate the science that keeps these beloved birds waddling into the future.
By investing in these research efforts, South Africa not only contributes to global conservation science but also highlights the importance of protecting our shared polar heritage. This International Penguin Day let’s celebrate the science that keeps these beloved birds waddling into the future.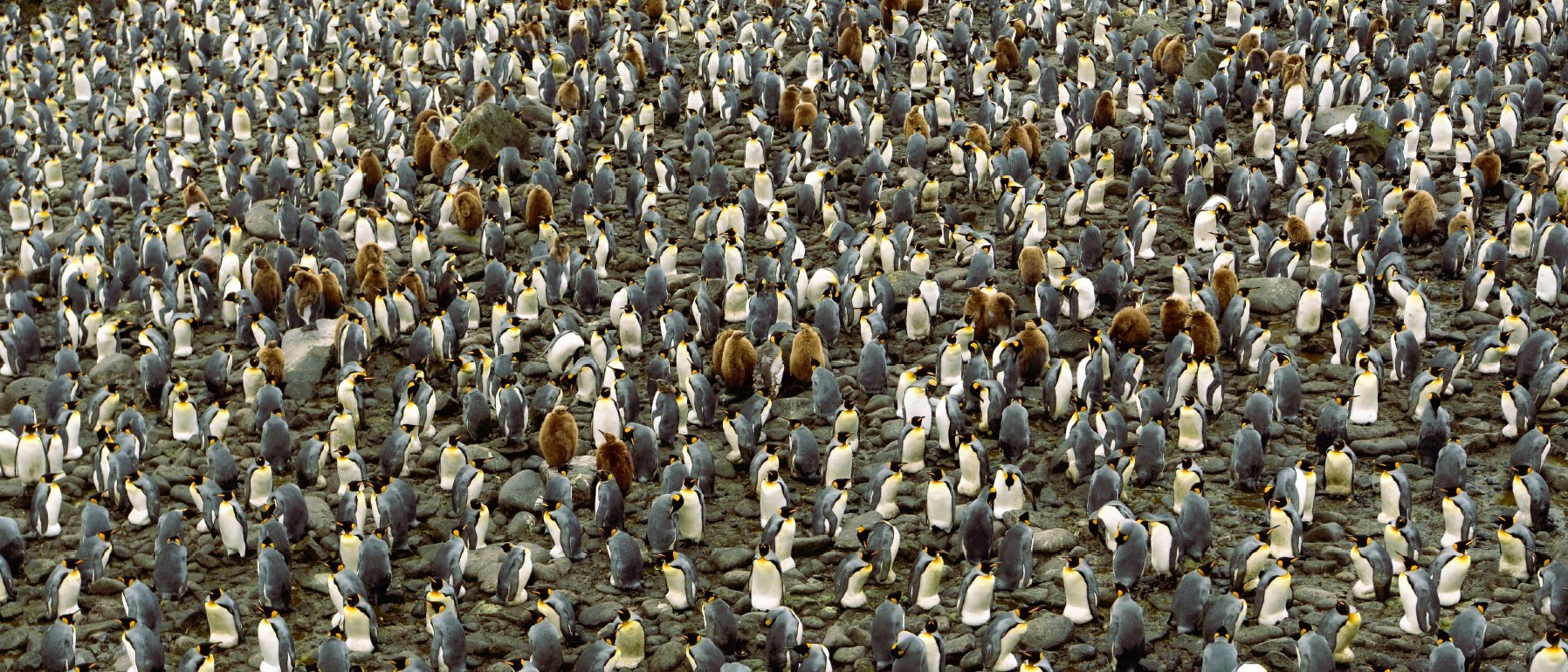

by Ria Olivier | May 11, 2024 | Ecology, International Days, Ornithology
 In 2024, World Migratory Bird Day will be celebrated on two days, 11 May and 12 October, aligning with the cyclic nature of
In 2024, World Migratory Bird Day will be celebrated on two days, 11 May and 12 October, aligning with the cyclic nature of  bird migration in different hemispheres. The World Migratory Bird Day campaign in 2024 will stress the need for proactive conservation measures. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilisers, and where possible, switching to organic farming. Other measures include maintaining and connecting areas of natural vegetation which provide food and shelter for birds and other species, in agricultural landscapes.
bird migration in different hemispheres. The World Migratory Bird Day campaign in 2024 will stress the need for proactive conservation measures. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilisers, and where possible, switching to organic farming. Other measures include maintaining and connecting areas of natural vegetation which provide food and shelter for birds and other species, in agricultural landscapes.

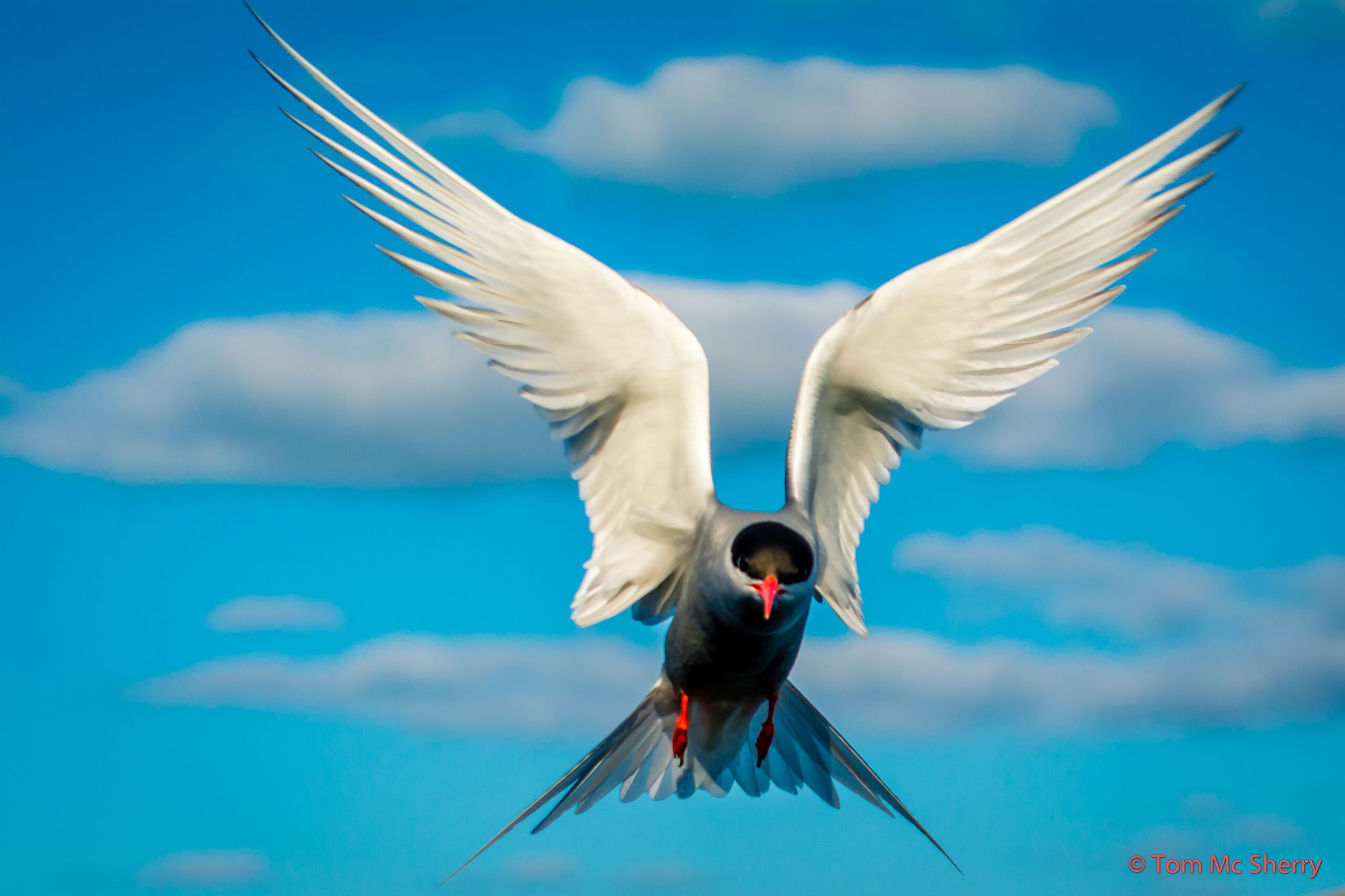
 Pictures of Antarctic Tern taken by Johan Bothma,1968 (left) and John Cooper, 1984 (right
Pictures of Antarctic Tern taken by Johan Bothma,1968 (left) and John Cooper, 1984 (right
“Birds are the most mobile organisms on the planet. Their ability to fly vast distances enables them to exploit predictable, short-term peaks in food availability. Almost one fifth of all birds undertake regular movements, usually tied to seasonal cycles. However, such large-scale movements also incur risks from commuting across the landscape. The balance between these costs and benefits determines who stays and who migrates. Recent studies suggest that migration promotes speciation, principally through the formation of sedentary daughter species” – Peter Ryan & Michelle Vrettos
 The Antarctic Tern’s closest relative is the Arctic Tern and it is likely that they evolved from Arctic Terns that settled in the south. Among other seabirds, it is less clear in which direction the radiation occurred. Species such as gannets and fulmars are not trans-equatorial migrants and so it is more likely that a few stragglers that crossed the equator established new populations in the opposite hemisphere. (article: “Stay or go? – Migration as an evolutionary driver”) (Arctic Tern, most famous for its long-distance migrations. Flying annually between the northern and southern hemispheres)
The Antarctic Tern’s closest relative is the Arctic Tern and it is likely that they evolved from Arctic Terns that settled in the south. Among other seabirds, it is less clear in which direction the radiation occurred. Species such as gannets and fulmars are not trans-equatorial migrants and so it is more likely that a few stragglers that crossed the equator established new populations in the opposite hemisphere. (article: “Stay or go? – Migration as an evolutionary driver”) (Arctic Tern, most famous for its long-distance migrations. Flying annually between the northern and southern hemispheres)
Colour Images by Tom McSherry taken on Gough Island in 2017
All images available on Antarctic Legacy of South Africa archive, contributed by Johan Bothma, John Cooper, Tom McSherry

 Every year on April 25th, we celebrate International Penguin Day—a global reminder of the unique role penguins plays in our planet’s ecosystems. These birds are not just symbols of the icy South—they are indicators of ocean health and climate change. From the sub-Antarctic islands to the Antarctic continent itself, penguins serve as sentinels of the sea, helping scientists track environmental shifts that affect us all.
Every year on April 25th, we celebrate International Penguin Day—a global reminder of the unique role penguins plays in our planet’s ecosystems. These birds are not just symbols of the icy South—they are indicators of ocean health and climate change. From the sub-Antarctic islands to the Antarctic continent itself, penguins serve as sentinels of the sea, helping scientists track environmental shifts that affect us all. South Africa plays a vital role in this mission through its National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), which supports long-term ecological research at key sites such as Gough Island, Marion Island, and Antarctica. These research stations are crucial hubs for studying penguin populations like the Northern Rockhopper on Gough Island and the Macaroni penguins on Marion Island. Scientists monitor breeding patterns, foraging behaviour, and survival rates—data that provide early warnings about oceanic changes. In Antarctica, SANAP researchers study Adélie and Emperor penguins, whose survival is intimately tied to the health of sea ice and krill populations.
South Africa plays a vital role in this mission through its National Antarctic Programme (SANAP), which supports long-term ecological research at key sites such as Gough Island, Marion Island, and Antarctica. These research stations are crucial hubs for studying penguin populations like the Northern Rockhopper on Gough Island and the Macaroni penguins on Marion Island. Scientists monitor breeding patterns, foraging behaviour, and survival rates—data that provide early warnings about oceanic changes. In Antarctica, SANAP researchers study Adélie and Emperor penguins, whose survival is intimately tied to the health of sea ice and krill populations. By investing in these research efforts, South Africa not only contributes to global conservation science but also highlights the importance of protecting our shared polar heritage. This International Penguin Day let’s celebrate the science that keeps these beloved birds waddling into the future.
By investing in these research efforts, South Africa not only contributes to global conservation science but also highlights the importance of protecting our shared polar heritage. This International Penguin Day let’s celebrate the science that keeps these beloved birds waddling into the future.


 In 2024,
In 2024,  bird migration in different hemispheres. The World Migratory Bird Day campaign in 2024 will stress the need for proactive conservation measures. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilisers, and where possible, switching to organic farming. Other measures include maintaining and connecting areas of natural vegetation which provide food and shelter for birds and other species, in agricultural landscapes.
bird migration in different hemispheres. The World Migratory Bird Day campaign in 2024 will stress the need for proactive conservation measures. This includes reducing the use of pesticides and fertilisers, and where possible, switching to organic farming. Other measures include maintaining and connecting areas of natural vegetation which provide food and shelter for birds and other species, in agricultural landscapes. 
 Pictures of Antarctic Tern taken by Johan Bothma,1968 (left) and John Cooper, 1984 (right
Pictures of Antarctic Tern taken by Johan Bothma,1968 (left) and John Cooper, 1984 (right The Antarctic Tern’s closest relative is the Arctic Tern and it is likely that they evolved from Arctic Terns that settled in the south. Among other seabirds, it is less clear in which direction the radiation occurred. Species such as gannets and fulmars are not trans-equatorial migrants and so it is more likely that a few stragglers that crossed the equator established new populations in the opposite hemisphere. (article: “
The Antarctic Tern’s closest relative is the Arctic Tern and it is likely that they evolved from Arctic Terns that settled in the south. Among other seabirds, it is less clear in which direction the radiation occurred. Species such as gannets and fulmars are not trans-equatorial migrants and so it is more likely that a few stragglers that crossed the equator established new populations in the opposite hemisphere. (article: “