by Ria Olivier | Apr 22, 2025 | International Days, Research, SANAP, Science
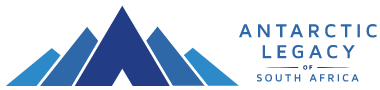
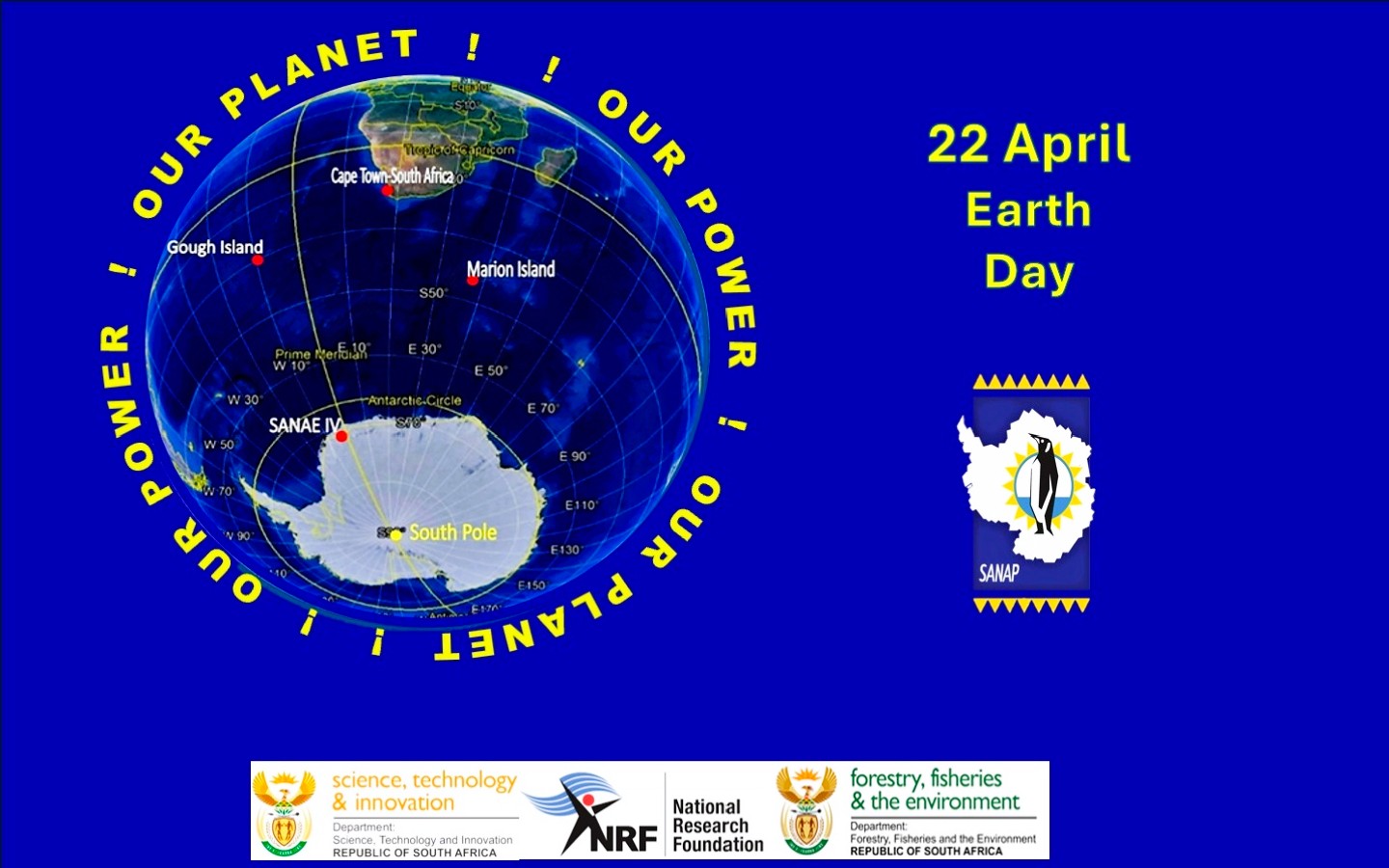 On Earth Day 2025, we recognize the vital role of science in securing the future of our planet. South Africa’s commitment to environmental stewardship is powerfully reflected in its research presence at Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island, under the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP). These remote, pristine locations serve as natural laboratories for understanding global climate systems, ocean circulation, and the health of marine ecosystems. From monitoring atmospheric carbon levels in Antarctica to studying biodiversity on Marion Island, South African researchers are gathering critical data that informs climate models, shapes conservation strategies, and guides global efforts to mitigate climate change.
On Earth Day 2025, we recognize the vital role of science in securing the future of our planet. South Africa’s commitment to environmental stewardship is powerfully reflected in its research presence at Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island, under the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP). These remote, pristine locations serve as natural laboratories for understanding global climate systems, ocean circulation, and the health of marine ecosystems. From monitoring atmospheric carbon levels in Antarctica to studying biodiversity on Marion Island, South African researchers are gathering critical data that informs climate models, shapes conservation strategies, and guides global efforts to mitigate climate change.
 The work conducted through SANAP not only enhances our understanding of Earth’s most vulnerable environments but also strengthens global collaboration on environmental sustainability. Long-term monitoring of weather patterns, sea temperatures, and wildlife populations across these islands contributes directly to international climate assessments and helps predict future planetary changes. As we mark Earth Day, let us celebrate the dedication of researchers who brave the extremes to ensure a liveable Earth for generations to come. Their efforts remind us that the answers to many of our environmental challenges lie in the farthest corners of our world—and that the time to act on them is now.
The work conducted through SANAP not only enhances our understanding of Earth’s most vulnerable environments but also strengthens global collaboration on environmental sustainability. Long-term monitoring of weather patterns, sea temperatures, and wildlife populations across these islands contributes directly to international climate assessments and helps predict future planetary changes. As we mark Earth Day, let us celebrate the dedication of researchers who brave the extremes to ensure a liveable Earth for generations to come. Their efforts remind us that the answers to many of our environmental challenges lie in the farthest corners of our world—and that the time to act on them is now.

by Ria Olivier | Mar 23, 2025 | Antarctica, Gough Island, International Days, Marion Island, Meteorology, Overwintering Team, Research

 Each year, on March 23rd, the global community observes World Meteorological Day, commemorating the establishment of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1950. This day highlights the pivotal role meteorology plays in ensuring the safety and well-being of societies worldwide. In 2025, we focus on the indispensable contributions of meteorologists stationed at the South African National Antarctic Programme’s (SANAP) remote research stations: SANAE IV in Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island.
Each year, on March 23rd, the global community observes World Meteorological Day, commemorating the establishment of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1950. This day highlights the pivotal role meteorology plays in ensuring the safety and well-being of societies worldwide. In 2025, we focus on the indispensable contributions of meteorologists stationed at the South African National Antarctic Programme’s (SANAP) remote research stations: SANAE IV in Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island.
 On this World Meteorological Day, we extend our gratitude to the meteorologists of SANAP’s overwintering teams. Their unwavering commitment and resilience in some of the most challenging environments ensure that we continue to deepen our understanding of Earth’s atmospheric processes, ultimately contributing to the safety and well-being of societies worldwide.
On this World Meteorological Day, we extend our gratitude to the meteorologists of SANAP’s overwintering teams. Their unwavering commitment and resilience in some of the most challenging environments ensure that we continue to deepen our understanding of Earth’s atmospheric processes, ultimately contributing to the safety and well-being of societies worldwide.
 SANAE IV (South African National Antarctic Expedition IV): Located at 71°S, 2°W in Antarctica, SANAE IV. Meteorological observations are conducted year-round, providing critical data on atmospheric conditions in this remote region.
SANAE IV (South African National Antarctic Expedition IV): Located at 71°S, 2°W in Antarctica, SANAE IV. Meteorological observations are conducted year-round, providing critical data on atmospheric conditions in this remote region.
Marion Island: Situated at 46°S, 37°E in the Southern Indian Ocean. The island’s meteorological station collects essential weather data, contributing to climate studies and aiding in the understanding of global weather patterns.
Gough Island: Located at 40°S, 9°W in the South Atlantic Ocean, Gough Island has hosted a South African weather station since 1956. The station conducts hourly climate observations and upper-air ascents, playing a crucial role in monitoring weather systems that can impact South Africa.
Meteorologists assigned to these stations undertake year-long deployments, known as overwintering periods, during which they perform several critical functions:
Surface Observations: Conducting regular measurements of temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other atmospheric parameters to monitor and document local weather conditions.
Upper-Air Observations: Launching weather balloons equipped with instruments to collect data on atmospheric pressure, temperature, and humidity at various altitudes, which is vital for understanding weather patterns and forecasting.
Equipment Maintenance: Ensuring that all meteorological instruments and equipment are calibrated and functioning correctly to maintain the accuracy and reliability of collected data.
Data Management: Recording, analyzing, and transmitting collected meteorological data to the South African Weather Service (SAWS) and other relevant organizations for use in weather forecasting and climate research.
The data collected by SANAP’s overwintering meteorologists contribute significantly to:
Weather Forecasting: Providing accurate and timely data that enhance the precision of weather forecasts, benefiting maritime navigation, aviation, and local communities.
Climate Research: Offering valuable insights into climate variability and change, particularly in the understudied southern hemisphere regions.
Environmental Monitoring: Supporting studies on the interactions between the atmosphere and the unique ecosystems of Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic islands, aiding in the conservation of these fragile environments.
by Ria Olivier | Feb 3, 2025 | Announcement, Geomorphology, Important Dates, Research, SANAP, SANAP Student, Science
 The International Conference on Geomorphology (ICG) 2025 is set to take place in breathtaking New Zealand, a land renowned for its dynamic landscapes and geological wonders. This global gathering of geomorphologists will provide a platform for cutting-edge discussions on landform processes, climate interactions, and Earth surface dynamics. We invite researchers, early-career scientists, and professionals to contribute to this exciting event by submitting abstracts to the special session:
The International Conference on Geomorphology (ICG) 2025 is set to take place in breathtaking New Zealand, a land renowned for its dynamic landscapes and geological wonders. This global gathering of geomorphologists will provide a platform for cutting-edge discussions on landform processes, climate interactions, and Earth surface dynamics. We invite researchers, early-career scientists, and professionals to contribute to this exciting event by submitting abstracts to the special session:
Geomorphological Insights from the Sub-Antarctic
Description: Sub-Antarctic islands, situated in the remote Southern Ocean, offer a unique geomorphological perspective due to their distinct geographical setting. These cold islands, characterized by both glacial and periglacial processes, provide crucial insights into the historical and ongoing changes in oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns within the southern hemisphere mid-latitudes. Unlike their northern hemisphere counterparts, these islands experienced a different Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) and complex deglaciation, leading to unique geomorphological features and processes. The landforms of these islands serve as invaluable proxies for understanding landscape responses to climate change. Palaeo-climatic shifts have profoundly influenced geomorphological and cryogenic dynamics, shaping landforms and influencing ecosystem processes. Contemporary climatic changes, such as rising temperatures, moisture fluctuations, and increased frequency of extreme events, pose significant threats to these delicate geomorphological systems. These changes have the potential to push landscape and ecosystem processes beyond their existing environmental thresholds, impacting landforms and biodiversity. This session aims to explore the geomorphological significance of Sub-Antarctic islands and their role as indicators of environmental change. We invite contributions that highlight the geomorphological processes and dynamics that shape the landscape of these Sub- Antarctic Islands. Research focusing on the region’s geomorphological responses to past and present climatic conditions and the possible implications for ecosystem processes are particularly welcome. Emerging researchers are encouraged to submit their work to advance our understanding of these critical sentinel landscapes.

 Who Should Submit?
Who Should Submit?
We strongly encourage early-career researchers, postgraduate students, and experienced scientists to contribute their work. This is an excellent opportunity to showcase your research to an international audience, gain valuable feedback, and network with leading experts in the field.
Abstract Submission Deadline: 31 May 2025!!
Don’t miss your chance to be part of ICG 2025 and contribute to this vital discussion on the evolving landscapes of the Sub-Antarctic.
 Message from Prof Werner Nel:
Message from Prof Werner Nel:
“Dear Friends and Colleagues, We are putting a session together for the International Conference on Geomorphology that will be held in Christchurch in February 2026. As you can see the session description is very open, so we can really put a nice diverse session together. We would like to ask you to consider submitting an abstract to the session.
Hope to see you there. All the best.” Werner Nel

by Ria Olivier | Oct 22, 2024 | Antarctica, Research, SA Polar Research Infrastructure, SANAP

 Antarctica, a pristine and remote frontier of scientific discovery, has long been a region of international interest for climate research, biodiversity, and understanding global environmental changes. In a recent meeting, held at SAEON Egagasini Node in Cape Town the event brought together South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) researchers and South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI) personnel to discuss how we can collaborate with the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute (AARI) to share resources, infrastructures and expertise to protect and study this unique region.
Antarctica, a pristine and remote frontier of scientific discovery, has long been a region of international interest for climate research, biodiversity, and understanding global environmental changes. In a recent meeting, held at SAEON Egagasini Node in Cape Town the event brought together South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP) researchers and South African Polar Research Infrastructure (SAPRI) personnel to discuss how we can collaborate with the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute (AARI) to share resources, infrastructures and expertise to protect and study this unique region.
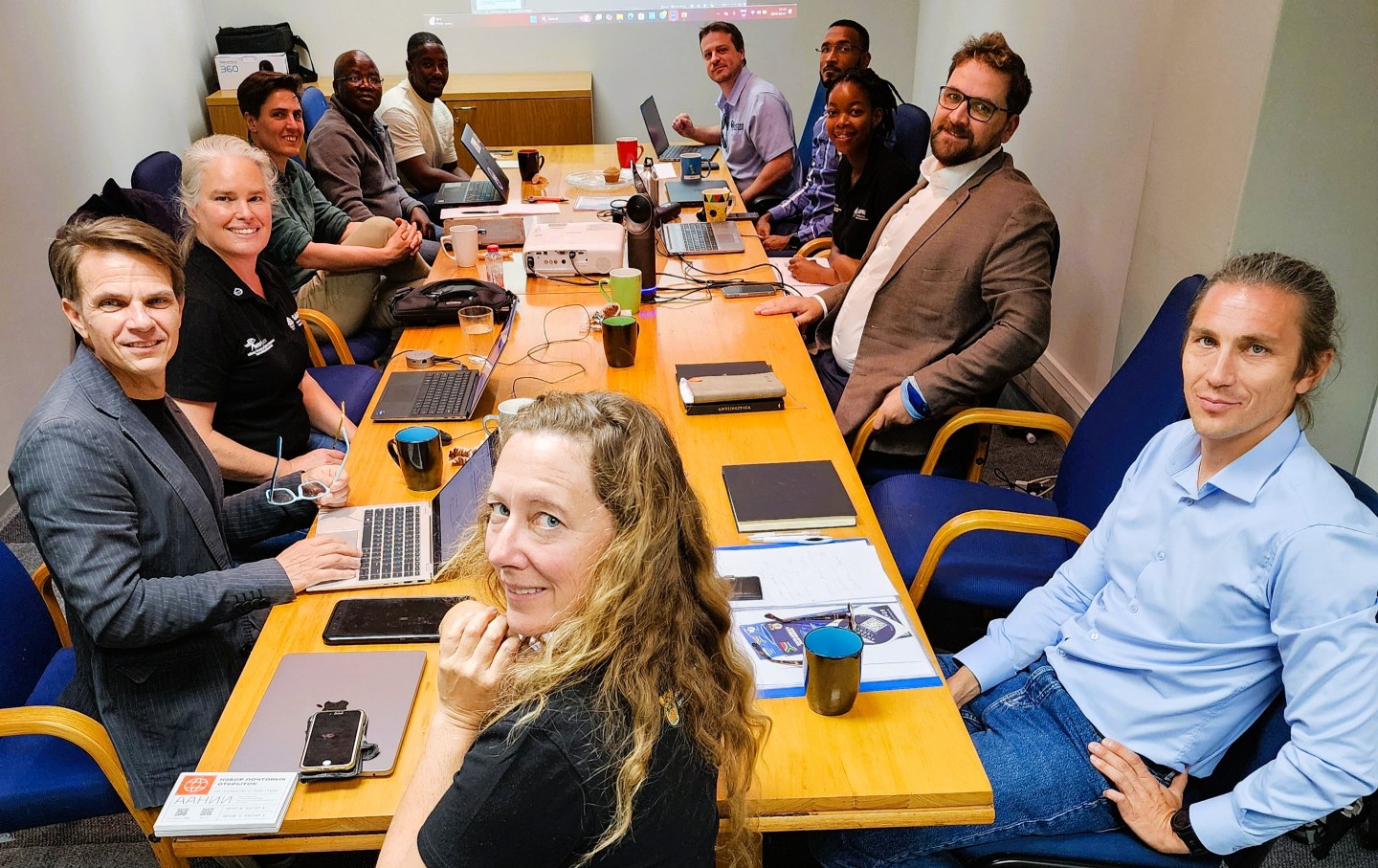 Attending in Person, Prof Juliet Hermes, Prof Marcello Vichi, Dr Anne Treasure, Ria Olivier, Dr Robyn Verrinder, Thomas Mtontsi, Steve Tebele, Jonathan Ward, Mark McKechnie, Rabia Mathakutha, Dr Sandy Thomalla, Dr Alexander Makarov, Dr Maxim Tatarkin
Attending in Person, Prof Juliet Hermes, Prof Marcello Vichi, Dr Anne Treasure, Ria Olivier, Dr Robyn Verrinder, Thomas Mtontsi, Steve Tebele, Jonathan Ward, Mark McKechnie, Rabia Mathakutha, Dr Sandy Thomalla, Dr Alexander Makarov, Dr Maxim Tatarkin
The meeting was focused on several aspects, including enhancing scientific cooperation in the Antarctic, and exploring ways to share logistical and research capacities. Both SANAP and AARI have a long history of involvement in Antarctic studies, and these discussions is a step forward in research and innovation collaboration.
 The meeting was in hybrid format and was attended online by Dr Michael Kosch, Dr David Hedding, Dr Geoff Grantham and Yinhla Shihlomule
The meeting was in hybrid format and was attended online by Dr Michael Kosch, Dr David Hedding, Dr Geoff Grantham and Yinhla Shihlomule
Dr Makarov introduced the activities, research and infrastructure of the AARI. He provided context to the visit and introduced AARI science and collaboration strategy. Highlights were the major directions of AARI are Meteorology, glaciology, Sea-ice research, Ice physics, ocean-atmosphere interaction, polar geography, geophysics, oceanography, interaction of ship hull with sea-ice, multi-year permafrost, hydrochemistry and hydrology of estuaries and water resources
Short presentations by the South African delegation with discussions followed (Presentations available on ALSA archive)
 The in-person presenters that started the South African Discussions and presenatations: Dr Sandy Thomalla – SOCCO, Rabia Mathakutha – SAPRI, Ria Olivier- ALSA, Dr Robyn Verrinder-MARIS
The in-person presenters that started the South African Discussions and presenatations: Dr Sandy Thomalla – SOCCO, Rabia Mathakutha – SAPRI, Ria Olivier- ALSA, Dr Robyn Verrinder-MARIS
 The following presentations were done:
The following presentations were done:
- SOCCO: South Africa’s ocean-climate science and innovation programme:
Taking ocean climate science to society. Sandy Thomalla.
- The South African Polar Research Infrastructure. Rabia Mathakutha
- An Overview of the Antarctic Legacy of South Africa Ria Olivier
- Antarctic MIZ Observations: Interdisciplinary approaches to resolve seasonal sea-ice variability. Robyn Verrinder
- Geology of Western Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica – a brief history of Geological Evolution insights. Geoffrey Grantham
- SANAP Geological Research program 2024-2026 in western Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Geoffrey Grantham
- Landscape and climate interactions in the sub-Antarctic. David Hedding
- SuperDARN HF radar at SANAE, Instrument infrastructure for space weather research. Michael Kosch
- SANSA – Jonathan Ward
- BRICS-RELAY and Antarctica InSync. Marcello Vichi
Through collaboration, we are expanding our ability to understand and protect one of the planet’s most critical ecosystems as Antarctica holds answers to some of the world’s biggest environmental questions, and through collaboration, we can unlock those answers.”
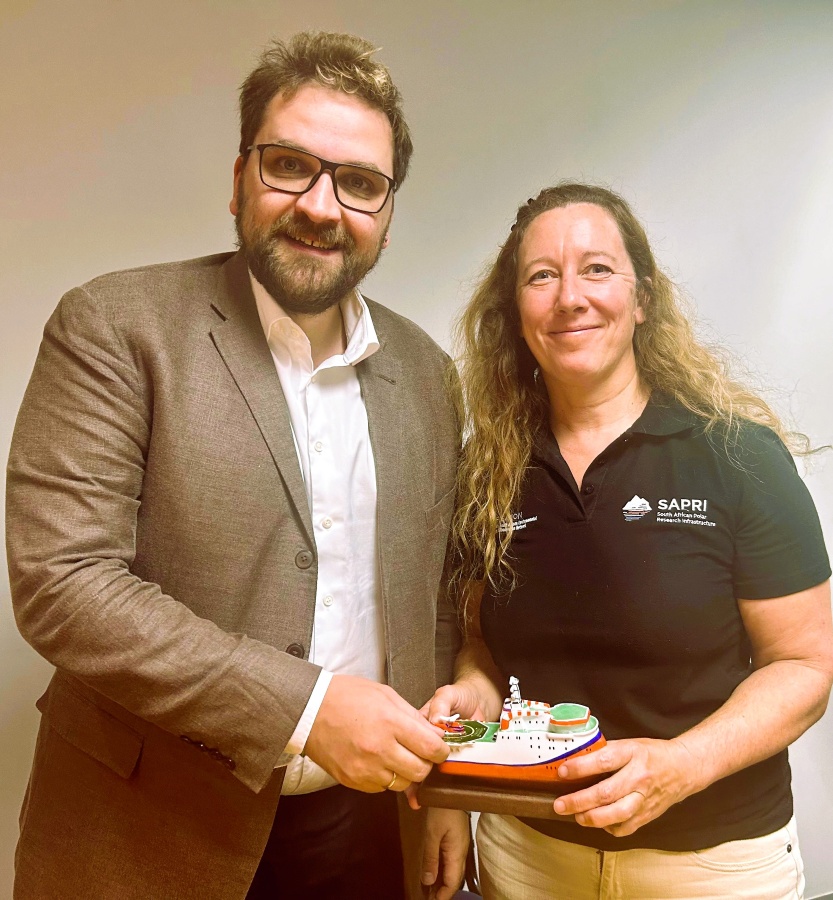 Dr Makarov present a gift to Prof Juliet Hermes of the ice resistant platform ‘North Pole’
Dr Makarov present a gift to Prof Juliet Hermes of the ice resistant platform ‘North Pole’
The discussion between AARI and SANAP and SAPRI signals a collaboration for Antarctic research, through shared resources, expertise, and data, both nations are poised to make significant contributions to global climate science. As the world watches the impacts of climate change unfold, this international collaboration offers hope for a deeper understanding of our planet and the preservation of its most fragile regions.

by Ria Olivier | Oct 21, 2024 | Announcement, Antarctica, Research
 You are invited to participate in an online mini symposium on Quaternary (including Holocene!) climate and environmental change in the Southern Hemisphere. This is an initiative by the WiSH (Warm Intervals in the Southern Hemisphere) group, an INQUA funded project. Whether your field is in archaeology, palaeontology, mathematics, palaeoclimate… or you are into developing new methods and techniques in modelling, multi-proxy dating etc., we would like to hear from you!
You are invited to participate in an online mini symposium on Quaternary (including Holocene!) climate and environmental change in the Southern Hemisphere. This is an initiative by the WiSH (Warm Intervals in the Southern Hemisphere) group, an INQUA funded project. Whether your field is in archaeology, palaeontology, mathematics, palaeoclimate… or you are into developing new methods and techniques in modelling, multi-proxy dating etc., we would like to hear from you!  The aim is to share recent research results and ideas related to Southern Hemisphere climatic and environmental change and variability, in particular during the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and in a range of environmental contexts. We especially encourage postgraduate students to attend and present! We have coordinated meetings for each Southern Hemisphere region, as follows, depending on where you work (not where you are based):
The aim is to share recent research results and ideas related to Southern Hemisphere climatic and environmental change and variability, in particular during the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and in a range of environmental contexts. We especially encourage postgraduate students to attend and present! We have coordinated meetings for each Southern Hemisphere region, as follows, depending on where you work (not where you are based):
- South American research community: 4 February 2025 (~9am-3pm Santiago, Chile, UTC-3), online, free of charge!
- Southern African research community: 5 February 2025 (~9am-3pm, Johannesburg, South Africa, UTC+2), online, free of charge!
- New Zealand and Australian research community: 6-8 February 2025, University of Canterbury Cass field station, in person, small charge applies.
In all instances, more information will follow.
To participate by presenting, please submit your abstract by 6 December 2024 using the template (click here to download) to the relevant regional contact below. Submissions can be made to:
If you would like to attend but not participate by presenting, this is absolutely fine, we will be sending meeting links for the S Am/SA online elements, but please indicate your intentions by just dropping an email to the relevant person. Feel free to contact us for any queries.
WiSH Steering Committee contact details:
South America:
Southern Africa:
Australasia:

by Ria Olivier | Oct 11, 2024 | Announcement, Jobs, Marion Island, News, Overwintering Team, Research, SANAP, Science, Southern Ocean, Stations, sub-Antarctic, Team member

The following positions are available on the sub-Antarctic, Marion Island for the overwintering period (April 2025 to May 2026)
Environmental Officer Assistant Environmental Officer
Communications Engineer Diesel Mechanic Electrical Engineer Medical Orderly
Senior Meteorological Technician Assistant Meteorological Technician
2 X Field Assistants – Sea Birds
Closing Date: 28 OCTOBER
Click here: View all positions

 On Earth Day 2025, we recognize the vital role of science in securing the future of our planet. South Africa’s commitment to environmental stewardship is powerfully reflected in its research presence at Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island, under the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP). These remote, pristine locations serve as natural laboratories for understanding global climate systems, ocean circulation, and the health of marine ecosystems. From monitoring atmospheric carbon levels in Antarctica to studying biodiversity on Marion Island, South African researchers are gathering critical data that informs climate models, shapes conservation strategies, and guides global efforts to mitigate climate change.
On Earth Day 2025, we recognize the vital role of science in securing the future of our planet. South Africa’s commitment to environmental stewardship is powerfully reflected in its research presence at Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island, under the South African National Antarctic Programme (SANAP). These remote, pristine locations serve as natural laboratories for understanding global climate systems, ocean circulation, and the health of marine ecosystems. From monitoring atmospheric carbon levels in Antarctica to studying biodiversity on Marion Island, South African researchers are gathering critical data that informs climate models, shapes conservation strategies, and guides global efforts to mitigate climate change. The work conducted through SANAP not only enhances our understanding of Earth’s most vulnerable environments but also strengthens global collaboration on environmental sustainability. Long-term monitoring of weather patterns, sea temperatures, and wildlife populations across these islands contributes directly to international climate assessments and helps predict future planetary changes. As we mark Earth Day, let us celebrate the dedication of researchers who brave the extremes to ensure a liveable Earth for generations to come. Their efforts remind us that the answers to many of our environmental challenges lie in the farthest corners of our world—and that the time to act on them is now.
The work conducted through SANAP not only enhances our understanding of Earth’s most vulnerable environments but also strengthens global collaboration on environmental sustainability. Long-term monitoring of weather patterns, sea temperatures, and wildlife populations across these islands contributes directly to international climate assessments and helps predict future planetary changes. As we mark Earth Day, let us celebrate the dedication of researchers who brave the extremes to ensure a liveable Earth for generations to come. Their efforts remind us that the answers to many of our environmental challenges lie in the farthest corners of our world—and that the time to act on them is now.


 Each year, on March 23rd, the global community observes World Meteorological Day, commemorating the establishment of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1950. This day highlights the pivotal role meteorology plays in ensuring the safety and well-being of societies worldwide. In 2025, we focus on the indispensable contributions of meteorologists stationed at the South African National Antarctic Programme’s (SANAP) remote research stations: SANAE IV in Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island.
Each year, on March 23rd, the global community observes World Meteorological Day, commemorating the establishment of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1950. This day highlights the pivotal role meteorology plays in ensuring the safety and well-being of societies worldwide. In 2025, we focus on the indispensable contributions of meteorologists stationed at the South African National Antarctic Programme’s (SANAP) remote research stations: SANAE IV in Antarctica, Marion Island, and Gough Island. On this World Meteorological Day, we extend our gratitude to the meteorologists of SANAP’s overwintering teams. Their unwavering commitment and resilience in some of the most challenging environments ensure that we continue to deepen our understanding of Earth’s atmospheric processes, ultimately contributing to the safety and well-being of societies worldwide.
On this World Meteorological Day, we extend our gratitude to the meteorologists of SANAP’s overwintering teams. Their unwavering commitment and resilience in some of the most challenging environments ensure that we continue to deepen our understanding of Earth’s atmospheric processes, ultimately contributing to the safety and well-being of societies worldwide. SANAE IV (South African National Antarctic Expedition IV): Located at 71°S, 2°W in Antarctica, SANAE IV. Meteorological observations are conducted year-round, providing critical data on atmospheric conditions in this remote region.
SANAE IV (South African National Antarctic Expedition IV): Located at 71°S, 2°W in Antarctica, SANAE IV. Meteorological observations are conducted year-round, providing critical data on atmospheric conditions in this remote region. The
The 
 Who Should Submit?
Who Should Submit? Message from Prof Werner Nel:
Message from Prof Werner Nel:

 Antarctica, a pristine and remote frontier of scientific discovery, has long been a region of international interest for climate research, biodiversity, and understanding global environmental changes. In a recent meeting, held at SAEON Egagasini Node in Cape Town the event brought together
Antarctica, a pristine and remote frontier of scientific discovery, has long been a region of international interest for climate research, biodiversity, and understanding global environmental changes. In a recent meeting, held at SAEON Egagasini Node in Cape Town the event brought together  Attending in Person, Prof Juliet Hermes, Prof Marcello Vichi, Dr Anne Treasure, Ria Olivier, Dr Robyn Verrinder, Thomas Mtontsi, Steve Tebele, Jonathan Ward, Mark McKechnie, Rabia Mathakutha, Dr Sandy Thomalla, Dr Alexander Makarov, Dr Maxim Tatarkin
Attending in Person, Prof Juliet Hermes, Prof Marcello Vichi, Dr Anne Treasure, Ria Olivier, Dr Robyn Verrinder, Thomas Mtontsi, Steve Tebele, Jonathan Ward, Mark McKechnie, Rabia Mathakutha, Dr Sandy Thomalla, Dr Alexander Makarov, Dr Maxim Tatarkin The meeting was in hybrid format and was attended online by Dr Michael Kosch, Dr David Hedding, Dr Geoff Grantham and Yinhla Shihlomule
The meeting was in hybrid format and was attended online by Dr Michael Kosch, Dr David Hedding, Dr Geoff Grantham and Yinhla Shihlomule The in-person presenters that started the South African Discussions and presenatations: Dr Sandy Thomalla – SOCCO, Rabia Mathakutha – SAPRI, Ria Olivier- ALSA, Dr Robyn Verrinder-MARIS
The in-person presenters that started the South African Discussions and presenatations: Dr Sandy Thomalla – SOCCO, Rabia Mathakutha – SAPRI, Ria Olivier- ALSA, Dr Robyn Verrinder-MARIS The following presentations were done:
The following presentations were done:  Dr Makarov present a gift to Prof Juliet Hermes of the ice resistant platform ‘North Pole’
Dr Makarov present a gift to Prof Juliet Hermes of the ice resistant platform ‘North Pole’
 You are invited to participate in an online mini symposium on Quaternary (including Holocene!) climate and environmental change in the Southern Hemisphere. This is an initiative by the WiSH (Warm Intervals in the Southern Hemisphere) group, an INQUA funded project. Whether your field is in archaeology, palaeontology, mathematics, palaeoclimate… or you are into developing new methods and techniques in modelling, multi-proxy dating etc., we would like to hear from you!
You are invited to participate in an online mini symposium on Quaternary (including Holocene!) climate and environmental change in the Southern Hemisphere. This is an initiative by the WiSH (Warm Intervals in the Southern Hemisphere) group, an INQUA funded project. Whether your field is in archaeology, palaeontology, mathematics, palaeoclimate… or you are into developing new methods and techniques in modelling, multi-proxy dating etc., we would like to hear from you!  The aim is to share recent research results and ideas related to Southern Hemisphere climatic and environmental change and variability, in particular during the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and in a range of environmental contexts. We especially encourage postgraduate students to attend and present! We have coordinated meetings for each Southern Hemisphere region, as follows, depending on where you work (not where you are based):
The aim is to share recent research results and ideas related to Southern Hemisphere climatic and environmental change and variability, in particular during the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and in a range of environmental contexts. We especially encourage postgraduate students to attend and present! We have coordinated meetings for each Southern Hemisphere region, as follows, depending on where you work (not where you are based):